Business COMPANY PORTFOLIO
FineAir Paving Block
Natural air purification system using photocatalytic activation reaction.
Photocatalyst is a substance that promotes photochemical reaction, and semiconductor, pigment, chlorophyll is one of them.
The principle of photocatalysis was proven by two Japanese scientists in 1967 and began to be put into practical use as a basic technology to help solve environmental issues.
It is used to purify the environment (to remove environmental pollution, to make antibacterial, deodorization, etc.) by using the function of oxidizing and decomposing harmful substances of photocatalyst, or to have self-cleaning effect utilizing a superhydrophilic function (a function of producing a thin film without making water droplets even when the surface is wet )to various products.
Patented technology of visible light photocatalyst
-
 Visible Light Sensitive Fe-TiO2 Photocatalytic Mechanism Controlled iron doping produces visible light absorption and photocatalytic activity through formation of 'band gap state'.
Visible Light Sensitive Fe-TiO2 Photocatalytic Mechanism Controlled iron doping produces visible light absorption and photocatalytic activity through formation of 'band gap state'. -
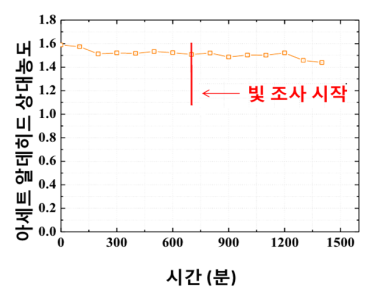
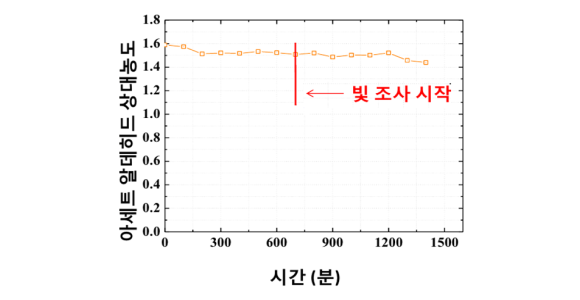 Ultraviolet sensitive TiO2 photocatalytic mechanism TiO2, which is not doped with iron, does not decompose acetaldehyde under visible light conditions.
Ultraviolet sensitive TiO2 photocatalytic mechanism TiO2, which is not doped with iron, does not decompose acetaldehyde under visible light conditions. -
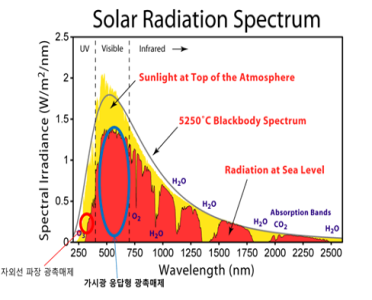
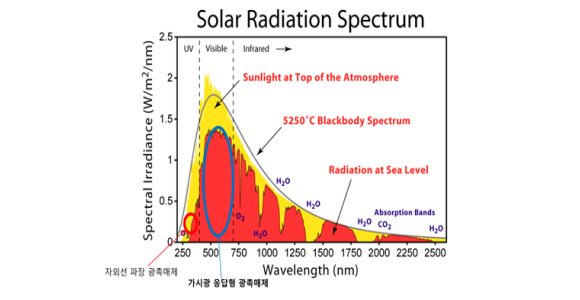 Solar energy spectrum The red part is about 80% of total solar energy as visible light.
Solar energy spectrum The red part is about 80% of total solar energy as visible light.
-
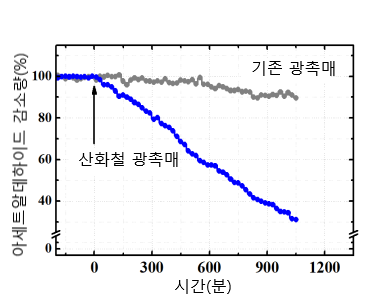
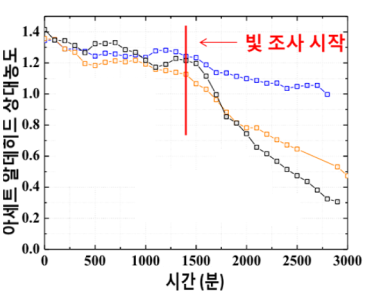
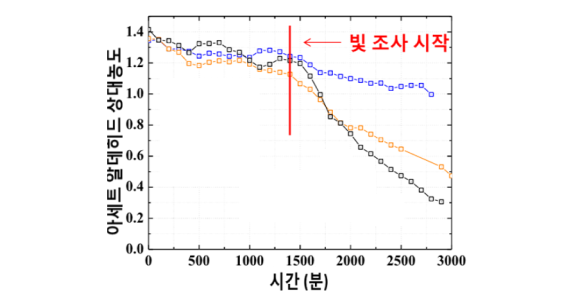
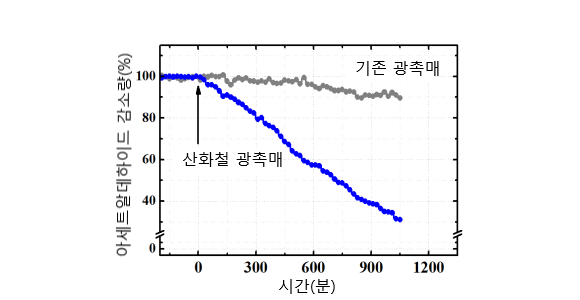 Experiment to measure acetaldehyde reduction with visible light. The reduction in acetaldehyde is about 7 times higher than that of conventional photocatalyst.
Experiment to measure acetaldehyde reduction with visible light. The reduction in acetaldehyde is about 7 times higher than that of conventional photocatalyst. -
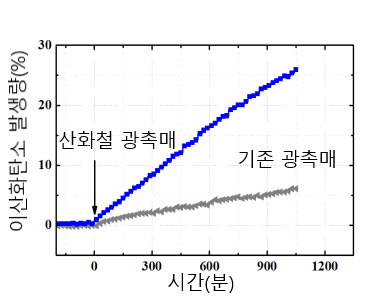
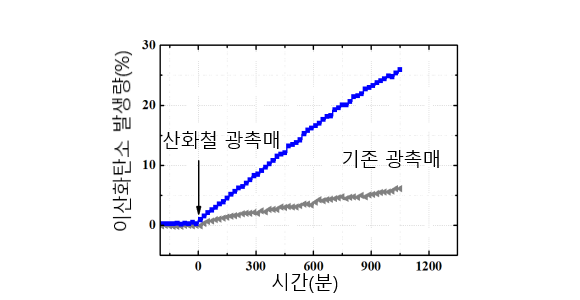 Experiment to measure carbon dioxide emission with visible light. Compared with conventional photocatalyst, it can be confirmed that volatile organic compounds are removed by about 5 times higher efficiency.
Experiment to measure carbon dioxide emission with visible light. Compared with conventional photocatalyst, it can be confirmed that volatile organic compounds are removed by about 5 times higher efficiency. -
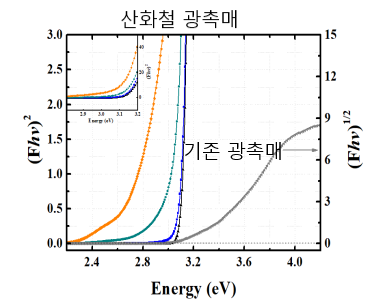
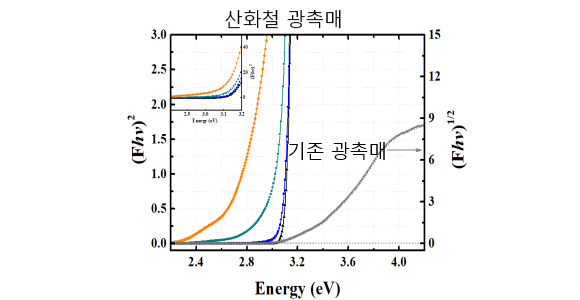 Experiment to measure solar energy absorption of photocatalytic. It can be confirmed that the absorption rate of the iron oxide photocatalyst is high.
Experiment to measure solar energy absorption of photocatalytic. It can be confirmed that the absorption rate of the iron oxide photocatalyst is high.

– Fine dust reduction through photocatalytic reaction.
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are well known as the causative agents of carcinogens and fine dusts. Nature&Environment Co, Ltd. cooperated with JH Global Co. to develop environmentally friendly air purification concrete block using photocatalytic material that adsorbs volatile organic compound, acetaldehyde with visible light . If installed at 5000m2, 50g of acetaldehyde can be decomposed per hour. Conventional photocatalytic technology decomposes harmful substances only in ultraviolet rays, which is a very small part of sunlight. However, this newly developed product can decompose harmful substances in visible light as well as ultraviolet light.
MBN etoday fnnews
As the only real time monitoring photocatalyst experiment equipment in Korea, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a surface-sensitive quantitative spectroscopic technique that measures the elemental composition at the parts per thousand range, empirical formula, chemical state and electronic state of the elements that exist within a material.

Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition. Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substance, or separating the different components of a mixture.









